리눅스 / 하드디스크 파디션 만들기, 포맷하기, 마운트하기
Created 2018-07-26
Last Modified 2024-01-05
리눅스에서 하드디스크 파티션 만들고, 포맷 하고, 마운트 하는 방법을 요약한다.
장착된 하드디스크 확인하기
- ls 명령어로 컴퓨터에 장착된 하드디스크 정보를 출력할 수 있다.
- /dev/sda, /dev/sdb 등이 하드디스크, /dev/sda1 등이 파티션이다.
# ls -l /dev/sd* brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 0 Oct 16 13:12 /dev/sda brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Oct 16 13:12 /dev/sda1 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 2 Oct 16 13:12 /dev/sda2 brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 16 Oct 16 13:12 /dev/sdb brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 32 Oct 16 13:12 /dev/sdc
- 파일시스템은 df -T 또는 blkid /dev/sd*로 확인할 수 있다. 마운트하지 않는 파티션에 대한 정보까지 알고 싶다면 후자를 사용한다.
파티션 만들기
- 파티션을 관리하는 명령어는 fdisk이다.
- /dev/sdb의 파티션을 관리하고 싶다면 다음과 같이 명령한다.
# fdisk /dev/sdb
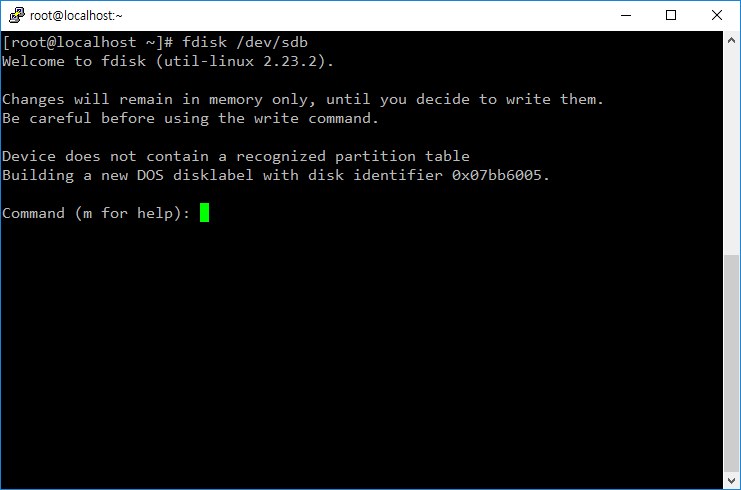
- 도움말이 필요하면 m을 입력한다.
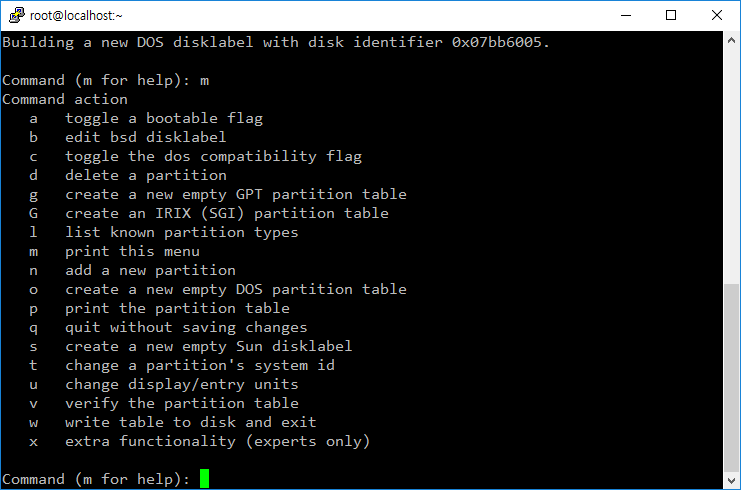
- 새 파티션은 n을 입력하고 안내에 따라 만든다.
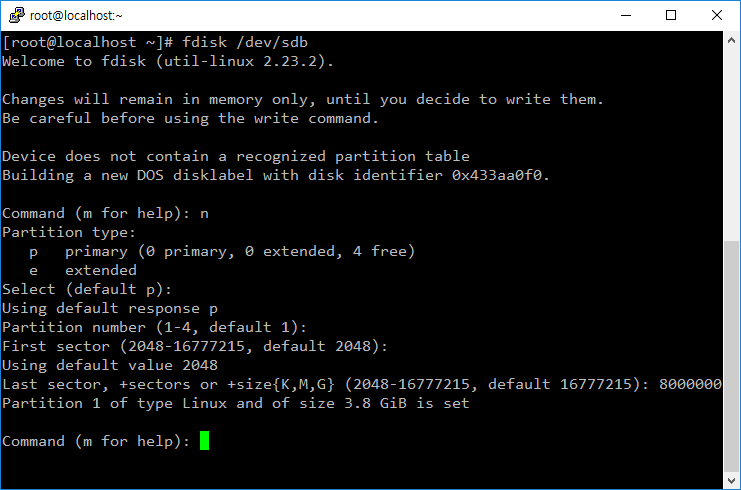
- w를 입력해야 변경사항이 반영된다.
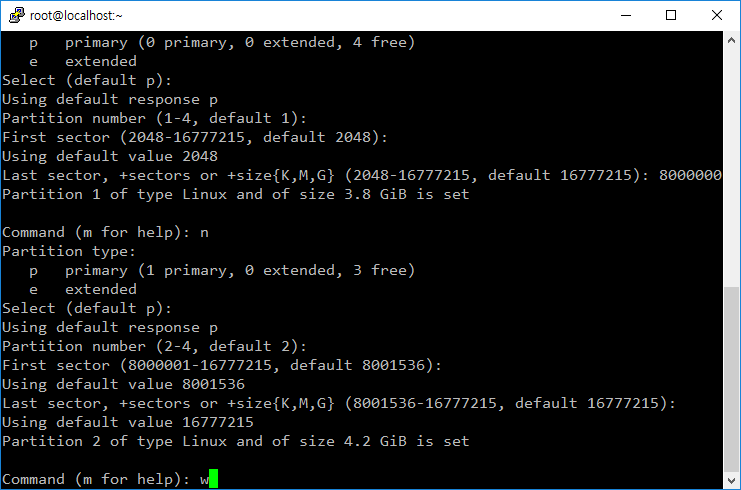
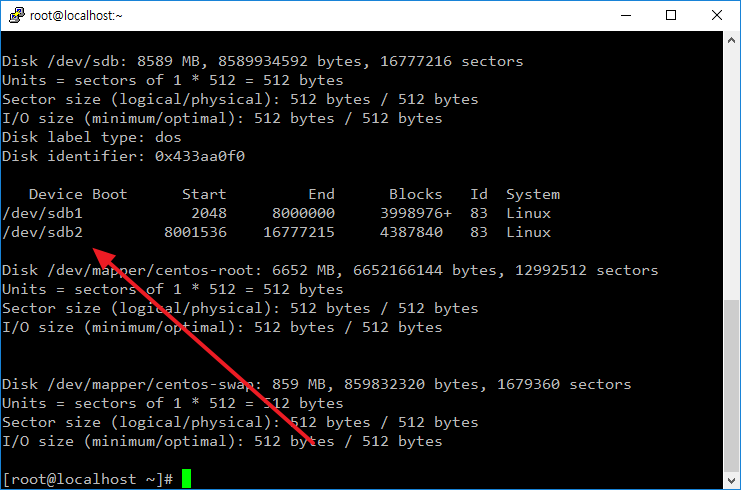
2TB 초과 하드디스크 파티션 만들기
2TB를 초과하는, 예를 들어 4TB 하드디스크를 장착하고 파티션을 만들려고 하면 다음과 같은 메시지를 보게 되고, 전체 디스크를 사용할 수 없다.
The size of this disk is 4 TiB (4398046511104 bytes). DOS partition table format cannot be used on drives for volumes larger than 2199023255040 bytes for 512-byte sectors. Use GUID partition table format (GPT).
이런 경우 g를 입력하여 GPT partition table을 만든 후 파티션을 만든다.
Command (m for help): g Created a new GPT disklabel (GUID: F13C6D0D-1E30-4448-B015-A61F3AE9EA48).
포맷하기
- 포맷하는 명령어는 mkfs이다.
- 예를 들어 /dev/sdb1 파티션을 ext4 파일 시스템으로 포맷하려면 다음과 같이 명령한다.
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
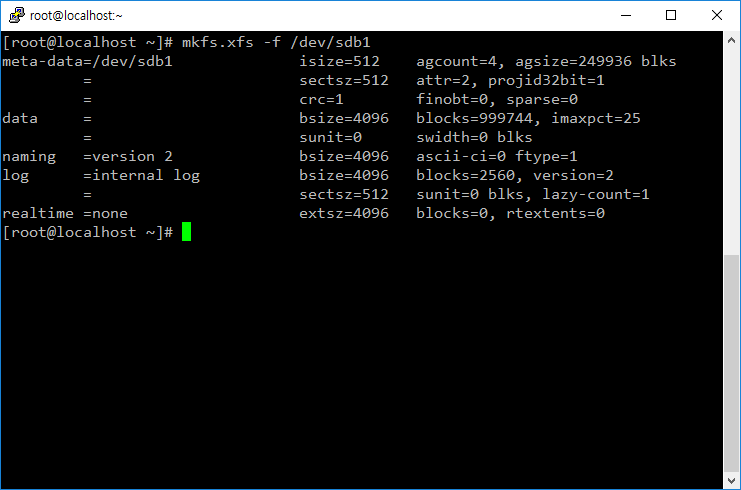
- 예를 들어 /dev/sdb1 파티션을 xfs 파일 시스템으로 포맷하려면 다음과 같이 명령한다.
# mkfs.xfs -f /dev/sdb1
- NTFS 파일 시스템으로 포맷하고 싶다면 mkntfs 명령어를 사용한다.
# mkntfs -f /dev/sdb1
- 파일 시스템은 df -T 또는 blkid /dev/sd*로 확인할 수 있다. 마운트하지 않는 파티션에 대한 정보까지 알고 싶다면 후자를 사용한다.
마운트하기
- 파티션을 특정 디렉토리에 연결해야 그 파티션을 사용할 수 있다.
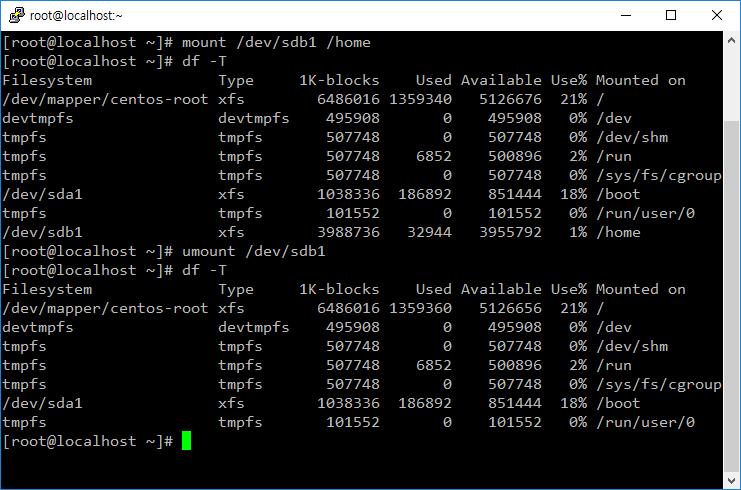
- 예를 들어 /dev/sdb1을 /home 디렉토리에 마운트하려면 다음과 같이 명령한다.
# mount /dev/sdb1 /home
- 마운트를 해제할 때는 umount 명령어를 사용한다.
# umount /dev/sdb1
- 부팅 시 자동으로 마운트되도록 하려면 /etc/fstab 파일에 다음과 같은 코드를 추가한다. /dev/sdb1 파티션을 /home 폴더에 마운트하라는 뜻이다. 파일 시스템 등 옵션은 적절히 변경한다.
/dev/sdb1 /home xfs defaults 0 0
- fstab 파일의 변경 내용을 바로 적용하고 싶다면 다음과 같이 명령한다.
# mount -a
UUID 사용하기
- 하드디스크에 /dev/sdb 같은 이름이 붙고, 파티션에는 /dev/sdb1 같은 이름이 붙는데, 이 이름이 고정된 것은 아니다. 하드디스크 장착 위치를 바꾸거나, 인식 순서가 바뀌면 그 이름도 바뀐다. 그런 경우 마운트가 제대로 되지 않을 수 있다. 그래서 마운트를 할 때는 하드디스크 고유값인 UUID를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- UUID는 blkid 명령으로 확인할 수 있다.
# blkid /dev/sda1: UUID="69d9add5-2153-4bc2-ad99-1560fb205c4b" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="aa61ba4b-01" /dev/sda2: UUID="PuMuNg-5YHg-qikJ-tc10-iPIM-7W1q-4fUqyc" TYPE="LVM2_member" PARTUUID="aa61ba4b-02" /dev/mapper/cl-root: UUID="79c8cfcb-c9e2-4243-8cf2-cf10eab57c40" TYPE="xfs" /dev/mapper/cl-swap: UUID="b69a5fc3-98db-4a27-b3d4-a7ef76244ad1" TYPE="swap" /dev/mapper/cl-home: UUID="fd372a6b-ee76-41d6-b7e6-6e6a7cf8193b" TYPE="xfs" /dev/sdb1: UUID="fd95c93f-03fc-418a-a6db-c26b921ec93b" TYPE="xfs" PARTUUID="e5f55ef6-01"
- /etc/fstab에 마운트 정보를 넣을 때
/dev/sdb1 /home xfs defaults 0 0
- 대신 다음처럼 한다.
UUID=fd95c93f-03fc-418a-a6db-c26b921ec93b /home xfs defaults 0 0