리눅스 / LVM / 만드는 방법, 수정하는 방법, 삭제하는 방법
Created 2021-10-10
Last Modified 2021-10-11
1TB 디스크와 2TB 디스크를 추가했다고 하자. 디스크 크기에 맞게 그대로 사용할 수도 있지만, 3TB 하나인 것처럼 사용하거나 1.5TB 두 개인 것처럼 사용하고 싶을 수도 있다. 즉, 물리적인 디스크 크기와 무관하게 자유롭게 볼륨을 만들고 싶은 것이다.
이럴 때 사용하는 것이 LVM(Logical Volume Manager)이다. 여러 개의 볼륨을 하나로 묶은 후 다시 배분하여 사용한다.(이렇게 만든 볼륨을 논리적 볼륨이라고 한다.)
LVM을 이용하여 논리적 볼륨을 만들고, 수정하고, 삭제하는 방법을 알아본다.
차례
LVM 만들기
LVM으로 볼륨을 만드는 순서는 다음과 같다.
- 물리적 볼륨을 만든다.
- 물리적 볼륨을 묶어서 볼륨 그룹을 만든다.
- 볼륨 그룹에 논리적 볼륨을 만든다.
간단한 예로 어떻게 구성하는지 알아보자. 목표는 100GB 디스크과 200GB 디스크로 50GB, 80GB, 170GB 볼륨을 만드는 것이다.
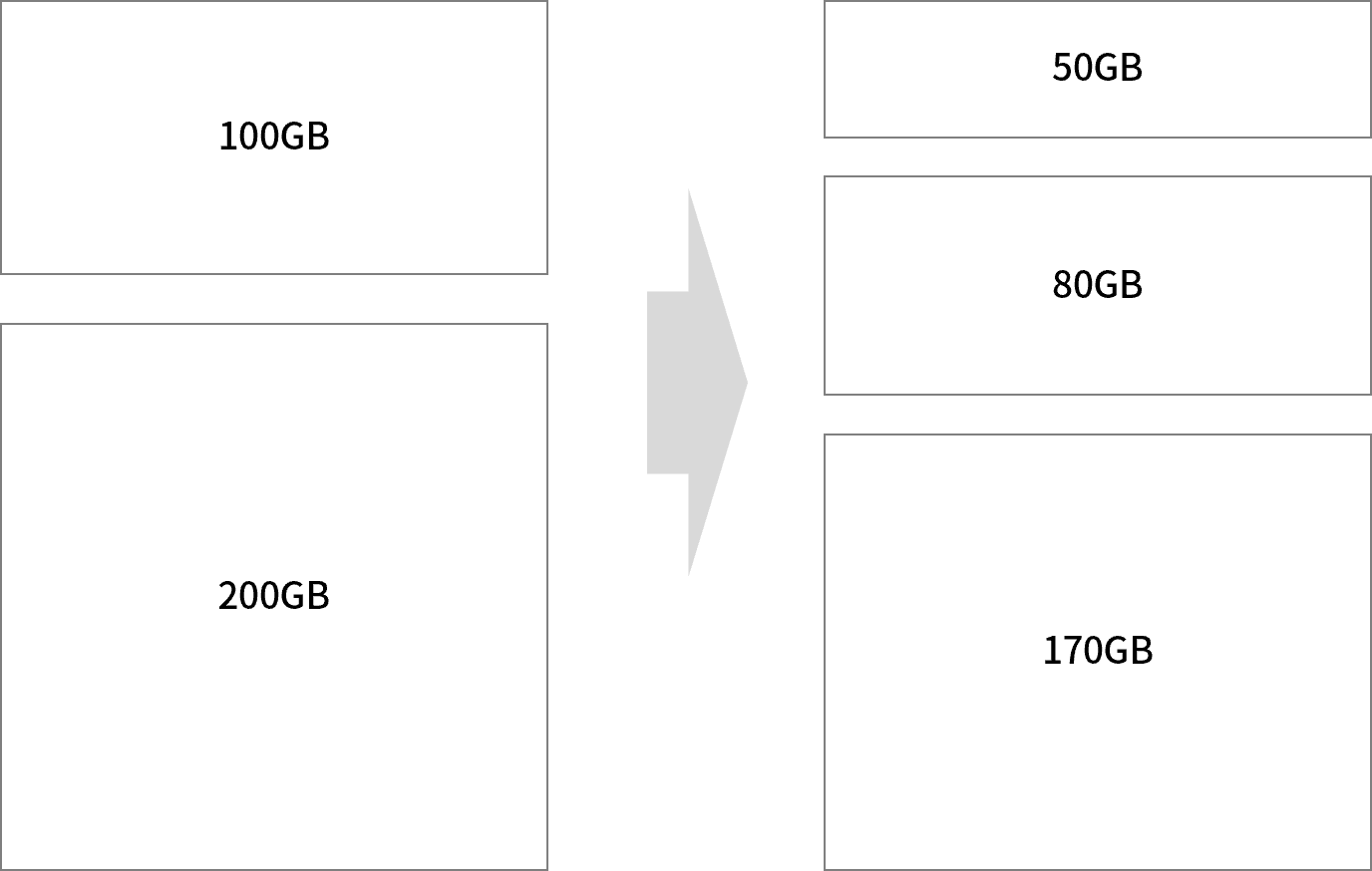
파티션 만들기
- 현재 상태는 다음과 같다. 디스크 두 개를 추가해서 /dev/sdb와 /dev/sdc가 생겼고, /dev/sdb의 크기는 100GB, /dev/sdc의 크기는 200GB이다.
# ls /dev/sd* /dev/sda /dev/sda1 /dev/sda2 /dev/sda3 /dev/sdb /dev/sdc
- fdisk로 파티션을 만든다. 주의할 점은 타입을 8e로 해야 한다는 것이다.
# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.34).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xa066b799.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-209715199, default 2048):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-209715199, default 209715199):
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 100 GiB.
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
- 파티션을 만든 후의 상태는 다음과 같다.
# ls /dev/sd* /dev/sda /dev/sda1 /dev/sda2 /dev/sda3 /dev/sdb /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc /dev/sdc1
물리적 볼륨 만들기
- /dev/sdb1과 /dev/sdc1로 물리적 볼륨(Physical Volume)을 만든다.
# pvcreate /dev/sdb1 Physical volume "/dev/sdb1" successfully created. root@ubuntu-2004-s-02:~# pvcreate /dev/sdc1 Physical volume "/dev/sdc1" successfully created.
볼륨 그룹 만들기
- /dev/sdb1과 /dev/sdc1를 볼륨 그룹으로 만든다.
- VG-01은 볼륨 그룹의 이름으로, 다른 것으로 만들어도 된다.
# vgcreate VG-01 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1 Volume group "VG-01" successfully created
논리적 볼륨 만들기
- VG-01 볼륨 그룹에 50GB 크기의 논리적 볼륨(Logical Volume)을 만든다.
- LG-01은 논리적 볼륨의 이름으로, 다른 것으로 만들어도 된다.
# lvcreate --size 50G --name LG-01 VG-01 Logical volume "LG-01" created.
- LG-02라는 이름의 80GB 크기의 논리적 볼륨을 만든다.
# lvcreate --size 80G --name LG-02 VG-01 Logical volume "LG-02" created.
- 나머지 공간을 다 사용하는 LG-03이라는 이름의 논리적 볼륨을 만든다.
# lvcreate --extents 100%FREE --name LG-03 VG-01 Logical volume "LG-03" created.
포맷하고 마운트하기
- 논리적 볼륨을 포맷한다. 아래는 LG-01을 EXT4 형식으로 포맷한 것이다.
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/VG-01/LG-01
mke2fs 1.45.5 (07-Jan-2020)
Creating filesystem with 13107200 4k blocks and 3276800 inodes
Filesystem UUID: ee2a0e20-db9f-4e38-b3d1-d46f00ccc215
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (65536 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
- 적당한 이름의 폴더를 만들고 마운트한다.
# mkdir /LG-01 # mount /dev/VG-01/LG-01 /LG-01
- 다음은 세 개의 논리적 볼륨을 포맷하고 마운트한 결과이다. 제일 아래 세 줄에 논리적 볼륨이 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on udev 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev tmpfs 394M 1.4M 393M 1% /run /dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv 196G 8.8G 178G 5% / tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/loop1 62M 62M 0 100% /snap/core20/1169 /dev/loop2 71M 71M 0 100% /snap/lxd/21029 /dev/loop3 68M 68M 0 100% /snap/lxd/21545 /dev/sda2 976M 112M 798M 13% /boot /dev/loop4 56M 56M 0 100% /snap/core18/2128 /dev/loop5 33M 33M 0 100% /snap/snapd/13170 /dev/loop0 62M 62M 0 100% /snap/core20/1081 /dev/loop6 33M 33M 0 100% /snap/snapd/12704 tmpfs 394M 36K 394M 1% /run/user/128 tmpfs 394M 0 394M 0% /run/user/0 /dev/mapper/VG--01-LG--01 49G 53M 47G 1% /LG-01 /dev/mapper/VG--01-LG--02 79G 57M 75G 1% /LG-02 /dev/mapper/VG--01-LG--03 167G 61M 158G 1% /LG-03
LVM 수정하기
볼륨 추가
볼륨 그룹에 볼륨을 추가하여 전체 공간을 확장할 수 있다. 위 예제에 이어 200GB 하드 디스크를 추가로 장착했다고 하면...
- 디스크를 추가하면 아래와 같은 상태가 된다. /dev/sdd가 추가한 디스크이다.
# ls /dev/sd* /dev/sda /dev/sda1 /dev/sda2 /dev/sda3 /dev/sdb /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc /dev/sdc1 /dev/sdd
- Linux LVM 파티션을 만든다.
# fdisk /dev/sdd
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.34).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table.
Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x8aa237e3.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
First sector (2048-419430399, default 2048):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-419430399, default 419430399):
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 200 GiB.
Command (m for help): t
Selected partition 1
Hex code (type L to list all codes): 8e
Changed type of partition 'Linux' to 'Linux LVM'.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
- 물리적 볼륨을 만든다.
# pvcreate /dev/sdd1 Physical volume "/dev/sdd1" successfully created.
- VG-01 볼륨 그룹에 추가한다.
# vgextend VG-01 /dev/sdd1 Volume group "VG-01" successfully extended
- 200GB의 여유 공간이 생긴다.
# vgdisplay VG-01 --- Volume group --- VG Name VG-01 System ID Format lvm2 Metadata Areas 3 Metadata Sequence No 9 VG Access read/write VG Status resizable MAX LV 0 Cur LV 3 Open LV 3 Max PV 0 Cur PV 3 Act PV 3 VG Size <499.99 GiB PE Size 4.00 MiB Total PE 127997 Alloc PE / Size 76798 / 299.99 GiB Free PE / Size 51199 / <200.00 GiB VG UUID YLV2F1-x00c-4CZt-LsCh-3q9O-iE3L-Ynx2vG
확장된 공간에 새로운 논리적 볼륨을 만들거나, 기존 논리적 볼륨의 크기를 늘릴 수 있다.
논리적 볼륨 확장하기
- lvextend 명령어로 논리적 볼륨의 크기를 확장한다. 아래는 /dev/VG-01/LG-01의 크기를 1GB 늘리는 것.
# lvextend -L+1G /dev/VG-01/LG-01 Size of logical volume VG-01/LG-01 changed from 50.00 GiB (12800 extents) to 51.00 GiB (13056 extents). Logical volume VG-01/LG-01 successfully resized.
- resize2fs 명령어로 파일 시스템의 크기를 확장해야 반영된다.
# resize2fs /dev/VG-01/LG-01 resize2fs 1.45.5 (07-Jan-2020) Filesystem at /dev/VG-01/LG-01 is mounted on /LG-01; on-line resizing required old_desc_blocks = 7, new_desc_blocks = 7 The filesystem on /dev/VG-01/LG-01 is now 13369344 (4k) blocks long.
- 아래는 /dev/VG-01/LG-01의 크기를 60GB로 늘리는 것. 마찬가지로 resize2fs 명령으로 파일 시스템 크기를 확장한다.
# lvextend -L60G /dev/VG-01/LG-01 Size of logical volume VG-01/LG-01 changed from 51.00 GiB (13056 extents) to 60.00 GiB (15360 extents). Logical volume VG-01/LG-01 successfully resized.
# resize2fs /dev/VG-01/LG-01 resize2fs 1.45.5 (07-Jan-2020) Filesystem at /dev/VG-01/LG-01 is mounted on /LG-01; on-line resizing required old_desc_blocks = 7, new_desc_blocks = 8 The filesystem on /dev/VG-01/LG-01 is now 15728640 (4k) blocks long.
LVM 삭제하기
LVM 삭제는 LVM 생성의 역순으로 진행한다.
논리적 볼륨 삭제하기
lvremove 명령어로 논리적 볼륨을 삭제한다. 아래는 /dev/VG-01/LG-03를 삭제하는 것.
# lvremove /dev/VG-01/LG-03 Do you really want to remove and DISCARD active logical volume VG-01/LG-03? [y/n]: y Logical volume "LG-03" successfully removed
볼륨 그룹 삭제하기
vgremove 명령어로 볼륨 그룹을 삭제한다. 아래는 VG-01을 삭제하는 것으로, 볼륨 그룹 안에 논리적 볼륨이 남아 있으면 삭제할 것인지 묻는다.
# vgremove VG-01 Do you really want to remove volume group "VG-01" containing 2 logical volumes? [y/n]: y Do you really want to remove and DISCARD active logical volume VG-01/LG-01? [y/n]: y Logical volume "LG-01" successfully removed Do you really want to remove and DISCARD active logical volume VG-01/LG-02? [y/n]: y Logical volume "LG-02" successfully removed Volume group "VG-01" successfully removed
물리적 볼륨 삭제하기
pvremove 명령어로 물리적 볼륨을 삭제한다. 아래는 /dev/sdd1을 삭제하는 것.
# pvremove /dev/sdd1 Labels on physical volume "/dev/sdd1" successfully wiped.

